

The area below the z curve starts from the left side of the graph.

State the percentage of score that lies below 73. The distribution of test scores has a mean of 80 and a standard deviation of 5.2.
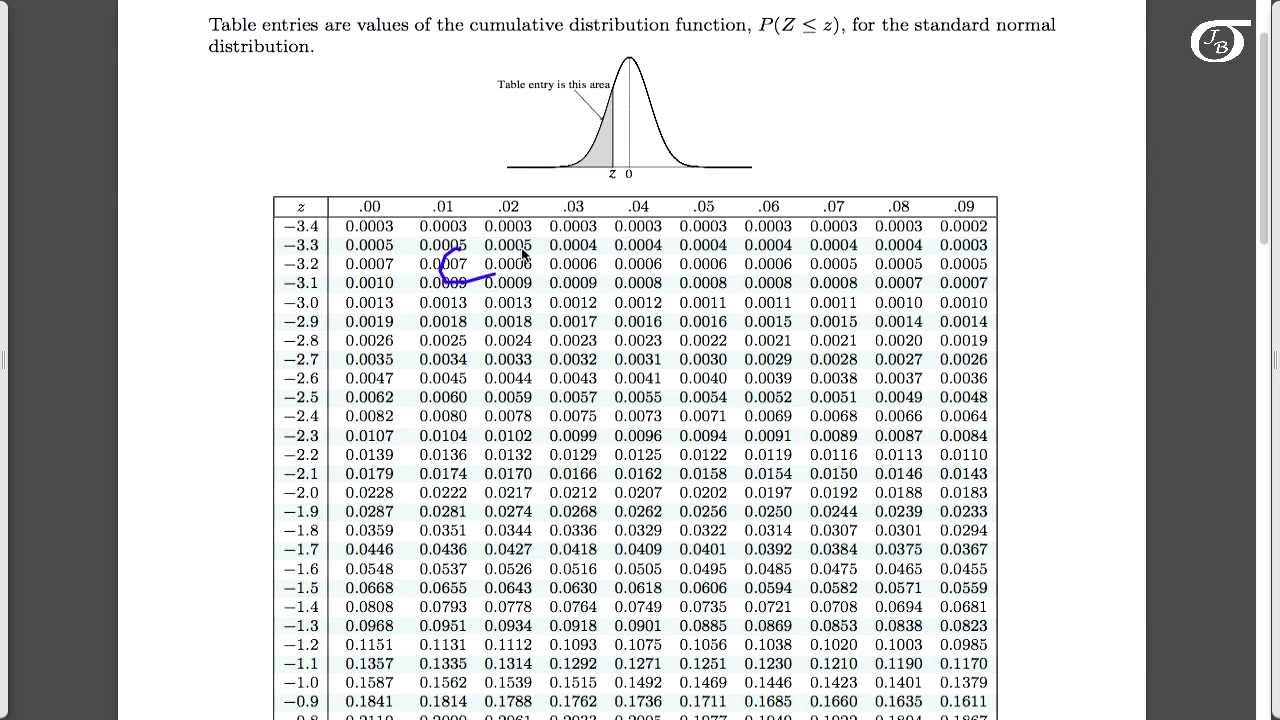
Let’s understand this concept with an example: Example1 It is equal to the area of the distribution above Z.
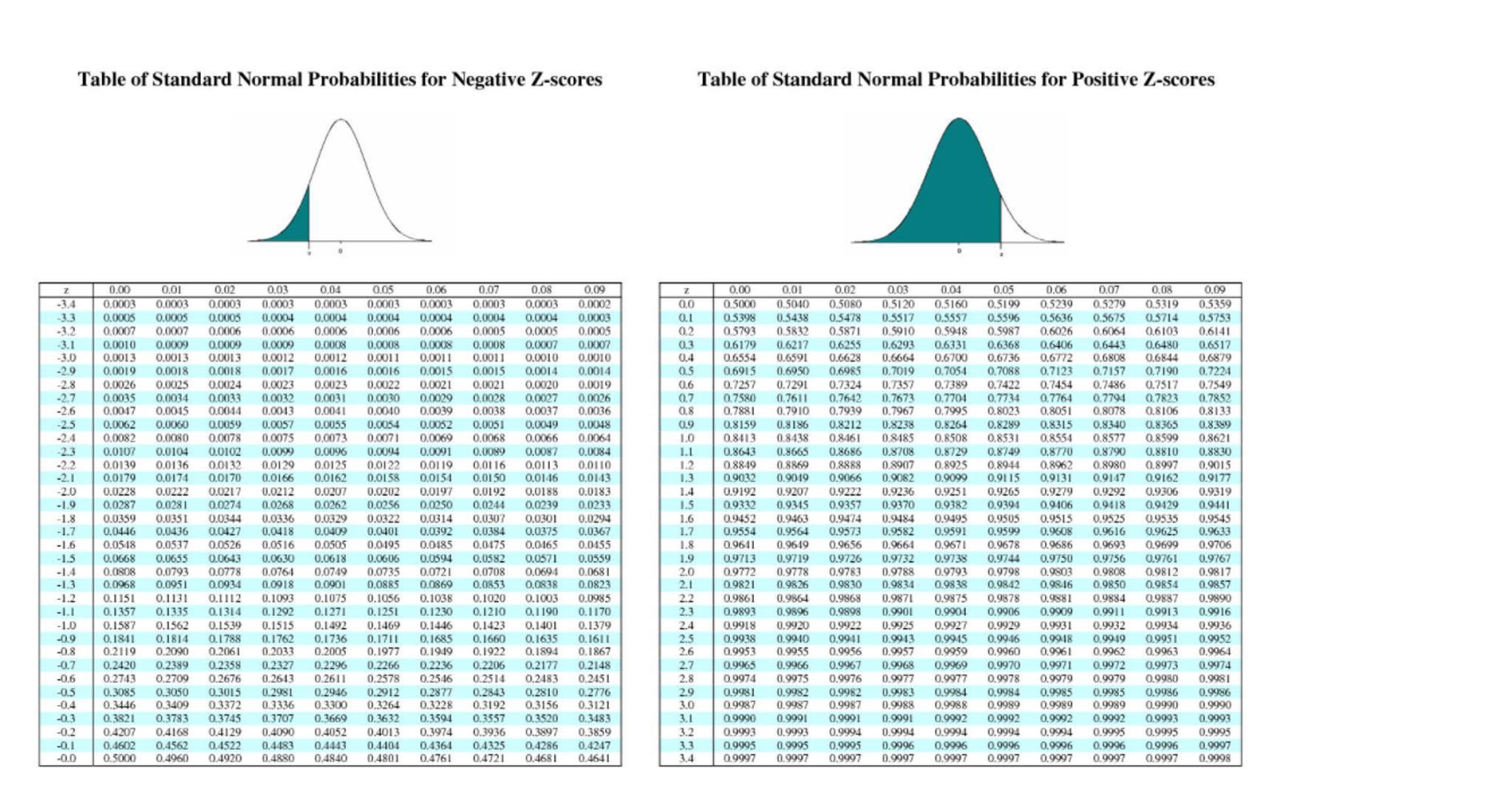
The area below the z curve is the one, that needs to be calculated. Don’t get confused with the right and left side of the mean. Here μ is the population mean, σ is the population standard deviation, and x is the sample size.Īfter this calculation, you need to look up in the table. The formula to convert a sample mean, X, to a z-score is: The left defines the negative values and the right shows the positive values. So, this approach makes better understanding as well as the solution to the problem. Now, the question arises about why there are two separate z tables? Because we have two values which are positive and negative. It is positive when it lies above the mean. Remember, the z- score shows the number of standard deviations where the value lies below the mean. Whether it is above, below, or between the values of normal distribution. It is using to find the probability of statistic value. He was a Belgian astronomer and he linked this distribution and the z curve. This phenomenon was first considered by Lambert Quetelet. It reflects the area of the z curve on the graph for standard deviations.įor instance, standard distribution is using to show the variables of height, weight, and strength. Z table is simply a standard normal distribution of percentage from 1 to 100. So, he devised a bell-shaped figure on the graph that we usually call the z curve. A French mathematician Abraham de Moivre was interested in gambling and used to find probabilities of the coin flips. Z table, an alphabetical term in the world of mathematics has its interesting origins from history.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
